Winter is knocking at our doorstep and we are hoping to get our brains worked out with some rigorous learning.
However the weather remains, as data analysts using SAS programming, we can definitely use the weather forecasts to provide the data for explaining the concepts of IF and IF-THEN-ELSE statements to our readers interested in learning SAS predictive modeling.
Our faculty at the SAS training centre in Delhi often get asked this simple question – what is the difference between the Sub-setting IF and the IF-THEN-ELSE-IF statements?
We understand that at an initial glance they do appear similar.
But you must understand that Sub-setting IF is a filter. And if you know about the WHERE clause, then it will be easy to understand for you as it is similar to the WHERE clause. It is used to filter or subset rows based on a certain condition. But it is still a little different from the WHERE clause as it has access to new variables as well when one’s constructing a data step.
The IF-THEN-ELSE-IF statement is known to most programmers, no matter whatever be there background. It is used to base an action based on a condition, however its role is not for sub-setting data.
To better understand the differences, here are the codes on the same:
Most SAS Certification institutions skimp on explaining the basics, but not us:
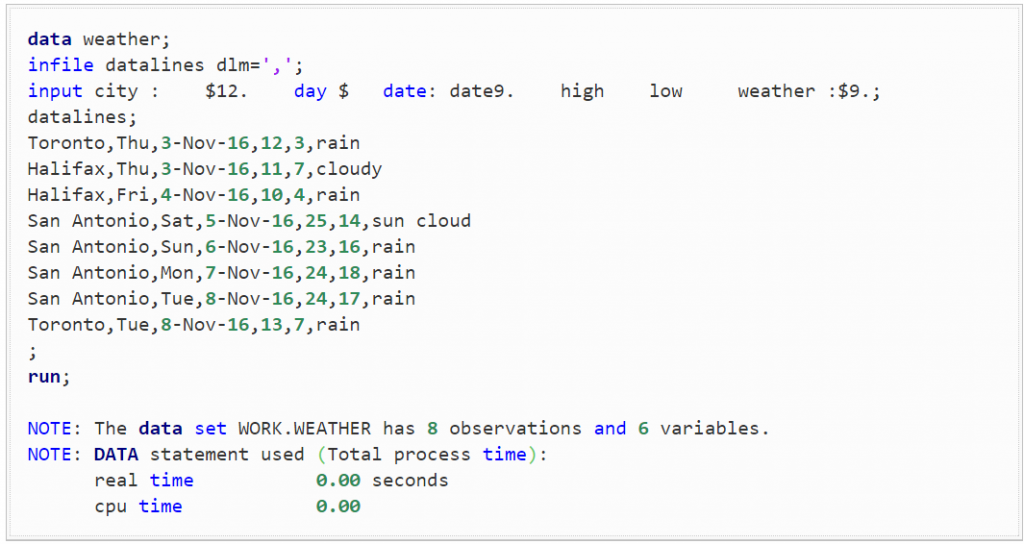
The first step is to construct the weather dataset by pulling them out the data from a simple Google Search.
Image Source: blogs.sas.com
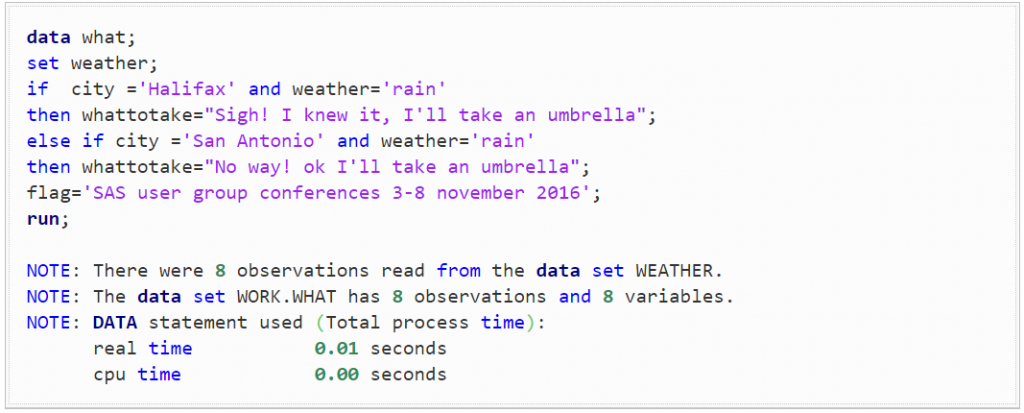
Step 2 is to run some conditional processing, notice the log note and how all the rows are put in to the output datasets:
Image Source: blogs.sas.com
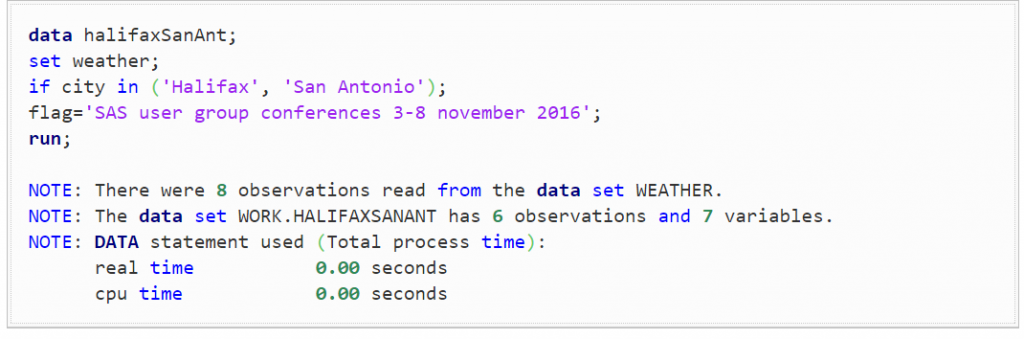
The third step involves making use of Sub-setting IF:
Image Source: blogs.sas.com
This will only work if the condition is true, and only will the next action will happen (i.e. flag will be set to SAS and more). The same works in the conditional processing scenario.
But the main driving difference will only be this – if only the Sub-setting IF condition is true (i.e. only if the city is San Antonio or Halifax) will SAS hit the RUN Statement.
In the RUN Statement, IMPLICIT are 2 actions, IMPLICIT output and IMPLICIT return.
And that is all you have in the difference between IF-THEN-ELSE statement and the Sub-setting IF statement.
Learn more about the differences in SAS statements with a SAS training course in Pune.
So, that is how a data analyst can prepare for the weather and know whether it will pour or shine!
For more SAS programming tips and updates on the best of SAS training courses drop by our website for regular uploads.
This post originally appeared on – blogs.sas.com/content/sastraining/2016/11/03/the-difference-between-the-subsetting-if-and-the-if-then-else-if-statement
Interested in a career in Data Analyst?
To learn more about Machine Learning Using Python and Spark – click here.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Advanced excel course – click here.
To learn more about Data Analyst with SAS Course – click here.
To learn more about Data Analyst with R Course – click here.
To learn more about Big Data Course – click here.
R Programming, SAS, Sas course, SAS Courses and R, SAS Predictive Modelling