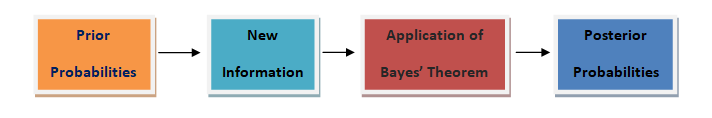
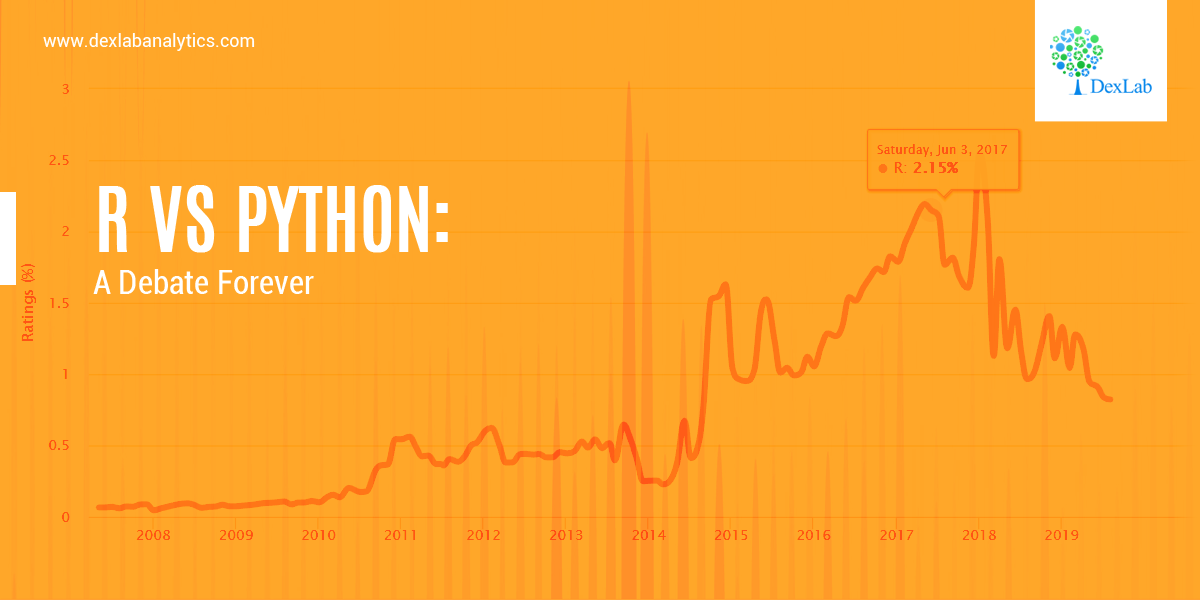
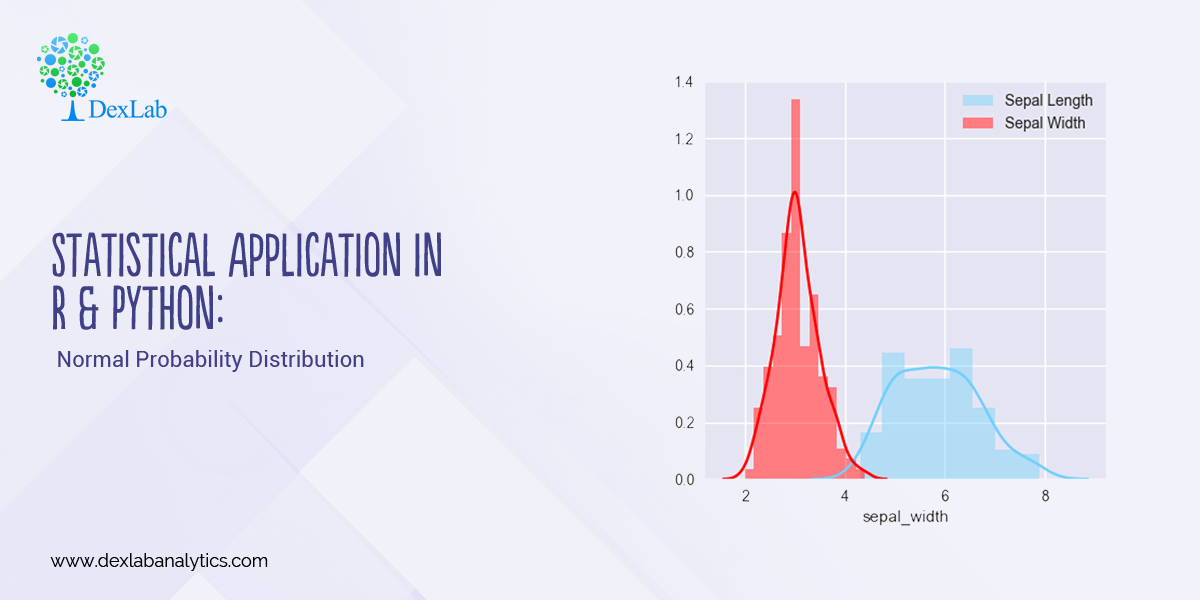
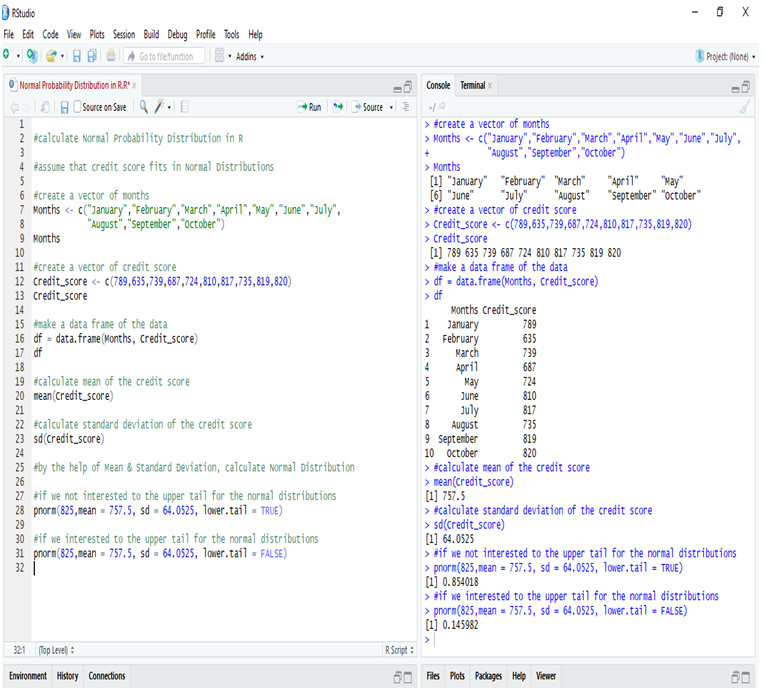
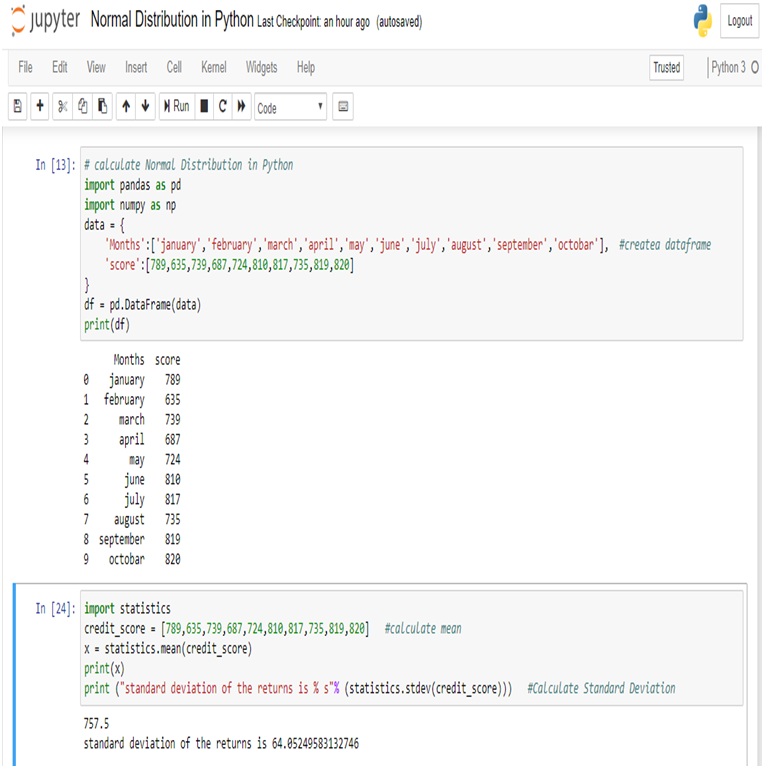
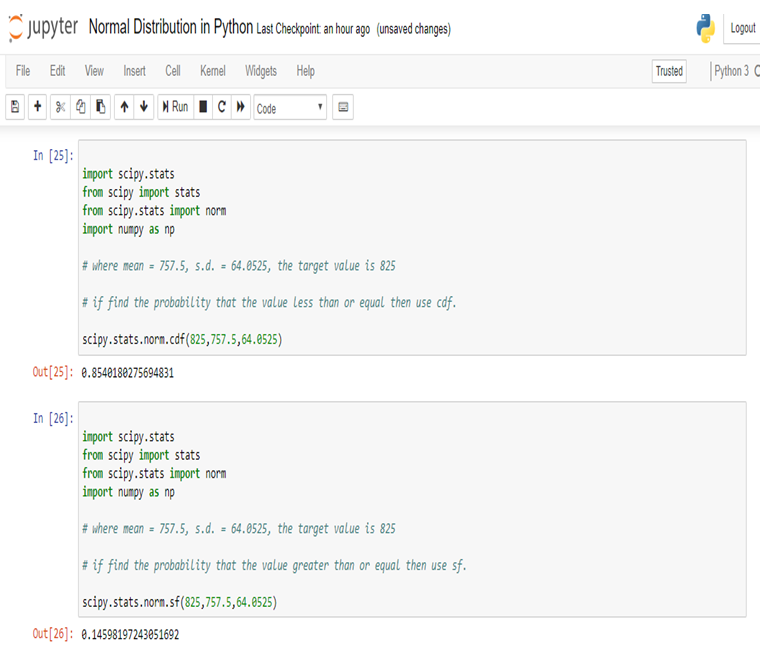
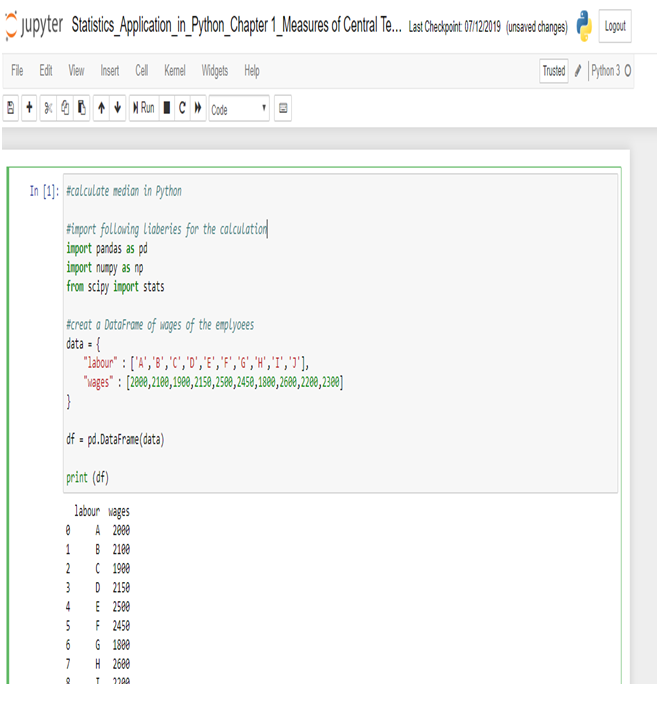
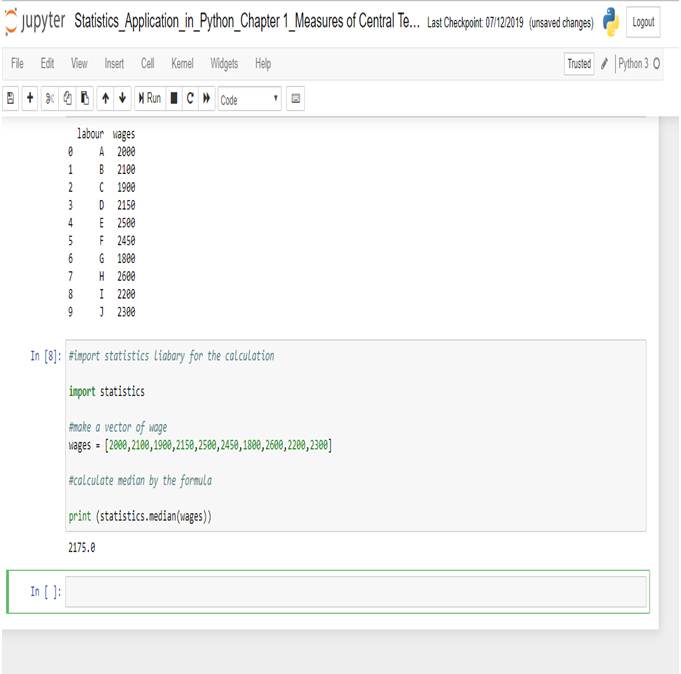
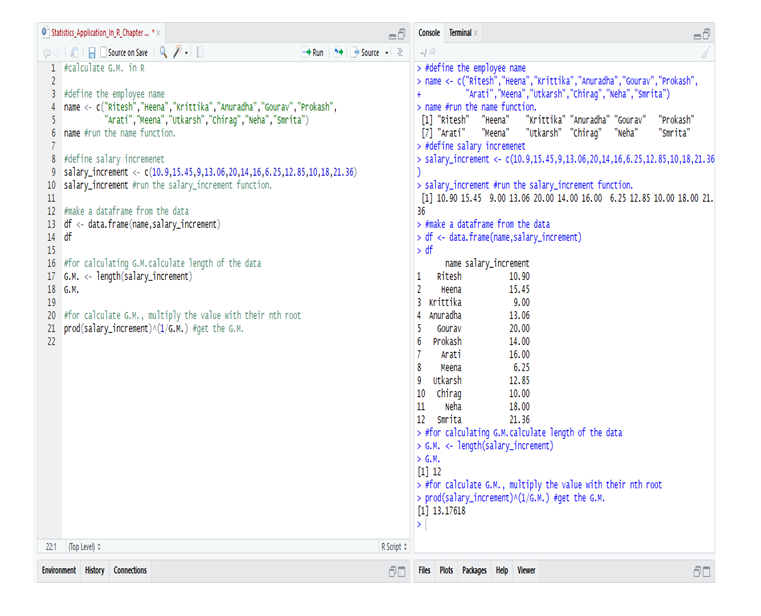
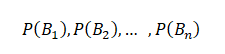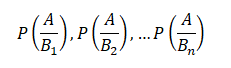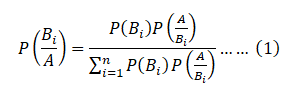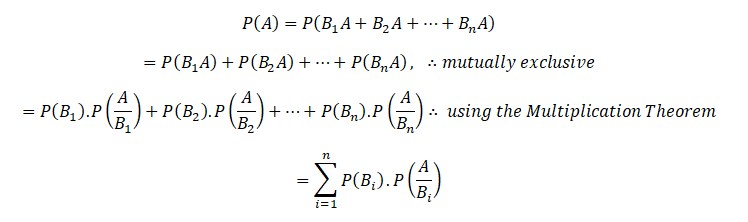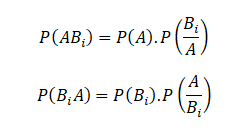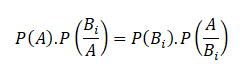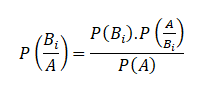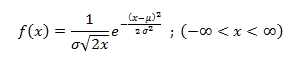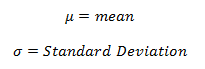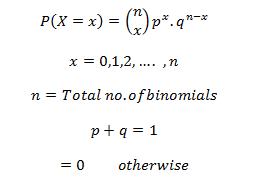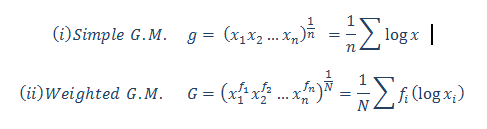The US economy, as it was officially announced by the United States National Bureau of Economic Research on June 8, entered a recession in February after hitting a peak of economic activity and growth. This is the first time the US economy has undergone a recession since the global financial crisis of 2008-09, says a report.
In the US alone, 19.6 lakh cases of covid-19 positive patients have been reported till date with 1.1 lakh cases of deaths recorded, the highest for any country in the world. In such a dire situation, the silver lining seems to be the fact that this recession, intensified by the lockdown that the country has imposed on itself to abate the spread of the disease, might be deep but short lived, The New York Times reported.
Irrespective of when the recession will end, poverty levels have already begun spiking the world over. The World Bank has said that, “the highest share of countries in 150 years would enter recessions at the same time. As many as 90% of the 183 economies () examined are expected to suffer from falling levels of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020, even more than the 85% of nations suffering from recession during the Great Depression of the 1930s”, The Guardian reported.
This will lead to dramatic rise in levels of poverty the world over. However, India might fare better on the global front for more reasons than one. Some economists feel “the (Indian) economy may do better than some other developing economies, which are heavily dependent on world trade” because of “lower dependence on exports (that) means less exposure to the decline in world trade. This and the low price of crude oil, our biggest import, may mean that we don’t suffer an external shock”.
In such circumstances, it is advisable that you stay home and not despair. Doing nothing but fretting will only add to your woes and not help the situation. Neither will binge-watching web series help. Instead, what you can do is ready yourself for a post COVID-19 world. You can do this by primarily upskilling yourself i.e.upgrading your skill set.
The only way to do this is remotely, though online classes available by the dozen. In fact, celebrities like Shakira have begun taking online classes (she in ancient philosophy) this lockdown while others like director Kevin Smith have finished old pending projects. The best skills to upgrade would, however, be those pertaining to computer science courses like big data, machine learning, deep learning or even credit risk modelling. These high-in-demand courses will look good on your résumé and instantly add to your employability wherever you plan to move to next.

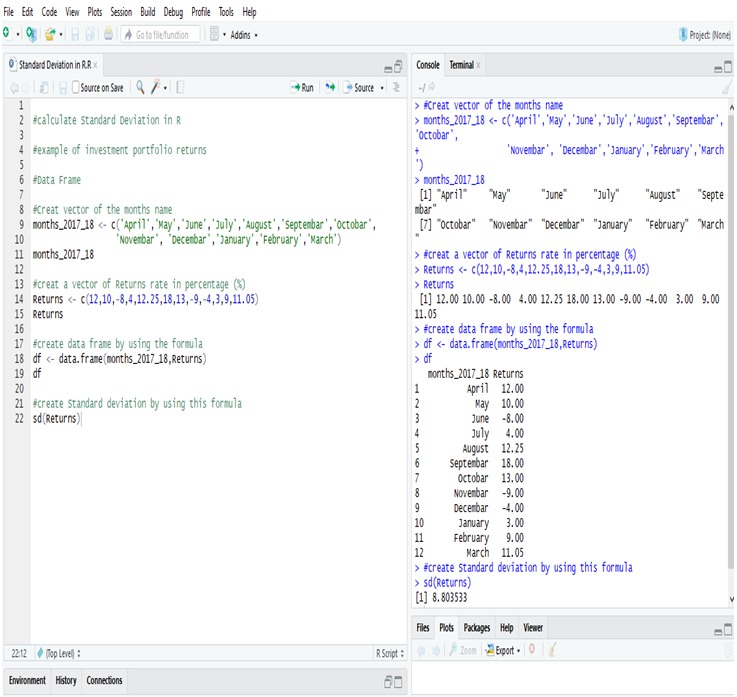
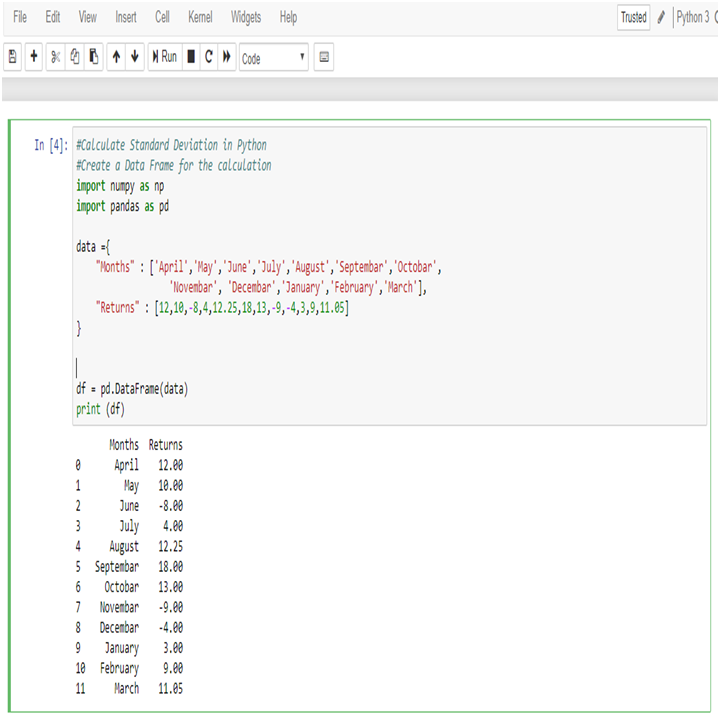
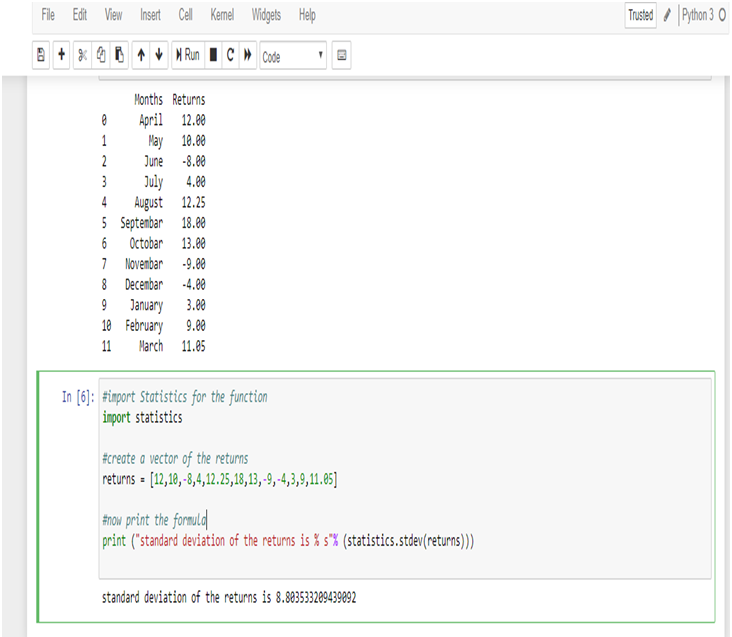
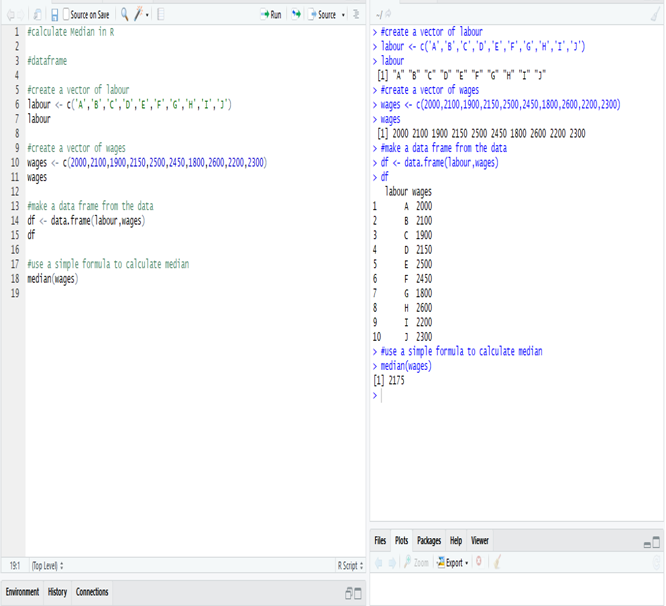
In India, DexLab Analytics, a premier institute offering some of the best credit risk modelling training courses and R programming courses in Gurgaon, suggests you try and learn a new programming language or enrol in a new business analytics course so your résumé stands stronger than it was before the lockdown. This will help you beat competition when you will be searching for work opportunities post the lockdown.
.