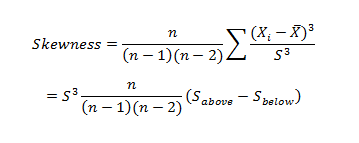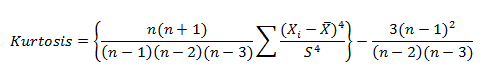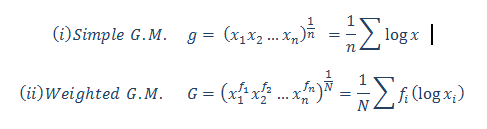Machine Learning is among a handful of technologies which we can see going on for long. It is a process or a technology which applies Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enable the machines/computers to learn things all by them and continue improving them subsequently.
Andrew Ng, a computer scientist from Stanford University, describes Machine Learning as the science which helps the computers to act without any explicit programming.
This new stream, as we are seeing it now, was originally conceived in the 1950s, however, it was not until the 21st century that Machine Learning started to revolutionise the world.
Several industries have already adopted this ground-breaking technology successfully to ensure the growth of their business. Moreover, this new technology has also boosted the demand for advanced programming languages, which were only rarely pursued earlier.
Here are some of the programming languages which seem quite promising with the rise of Machine Learning:
Python
This high-level programming language dates back to the early 1990s and has been widely popular since then, for Data Science, back-end development and Deep Learning for computer vision with Python. Python for data analysis is regarded as a powerful tool and is actively used in Big Data Technology.
R
R has been developed in the 1990s along with Python and was a part of the GNU project. Ever since it was discovered, R finds its uses extensively in Data Analysis, Machine Learning and the development of Artificial Intelligence. Furthermore, R is revered by the world of statisticians.
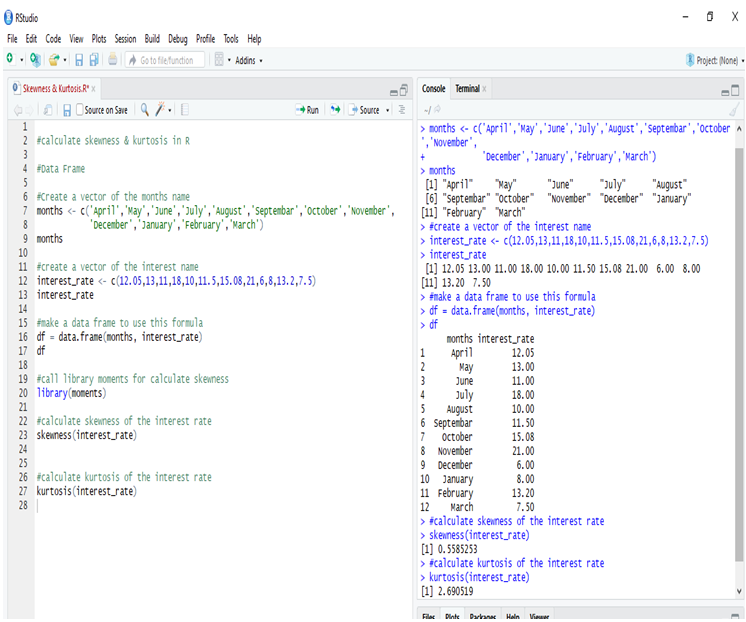
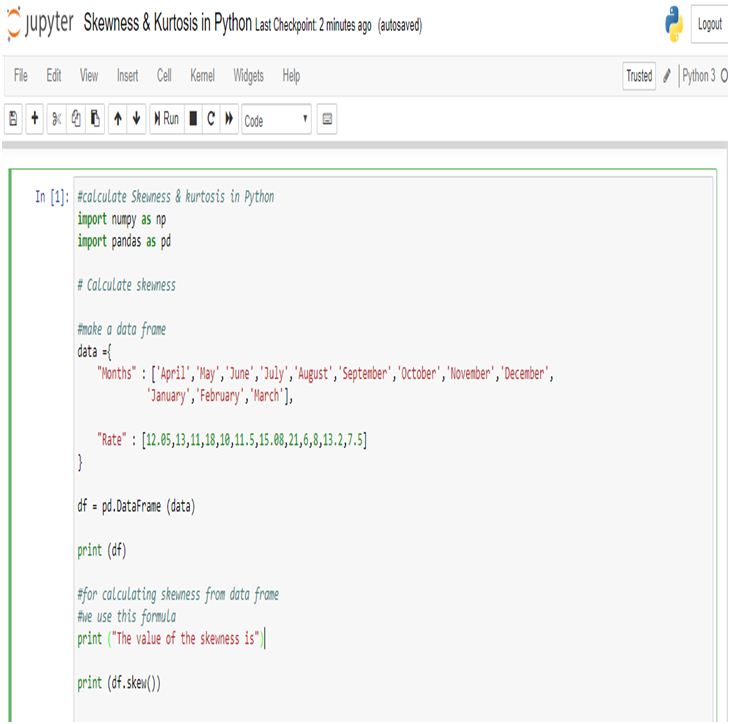
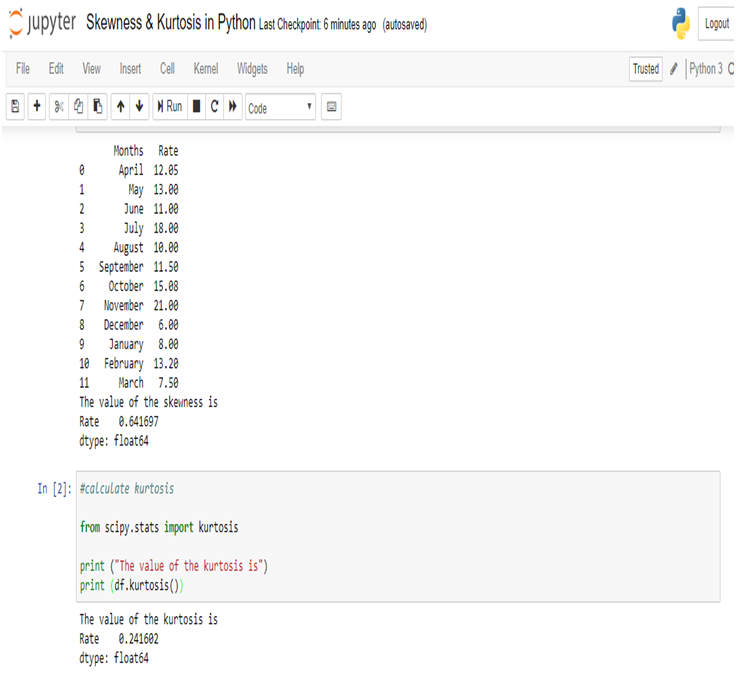
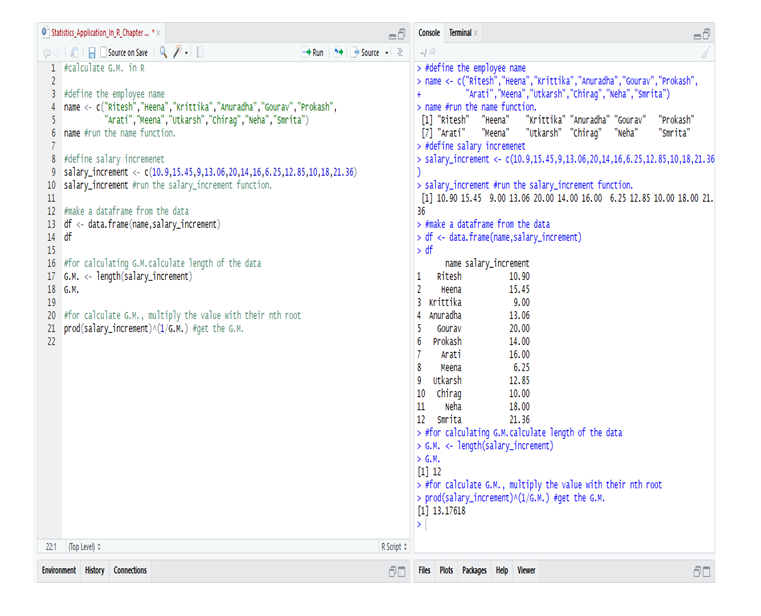
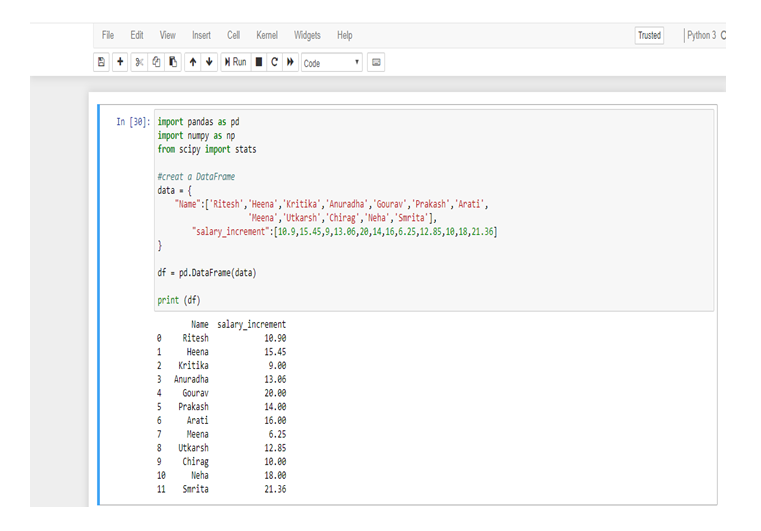
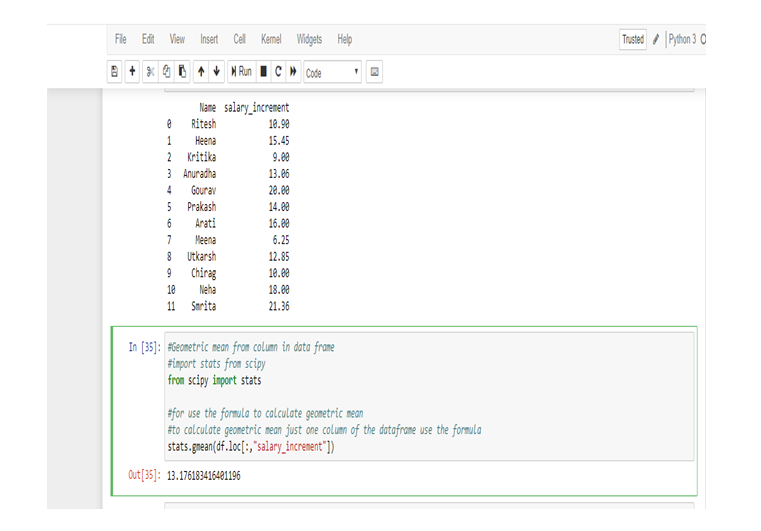
Application to R and Python are effectively used to calculate the Arithmetic mean, Harmonic mean, Geometric Mean, Skewness & Kurtosis. Statistical Application Of R & Python: Know Skewness & Kurtosis And Calculate It Effortlessly shows you the way how.
JavaScript, C++, Java are some other notable programming languages that are dominant. So, hurry up and join the exclusive computer vision course Python now. With Dexlab Analytics, a formidable institute in the Big Data Analytics industry, you can enroll for our tailor-made Artificial Intelligence course in Delhi with just a click from the comfort of your house.
Interested in a career in Data Analyst?
To learn more about Data Analyst with Advanced excel course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with R Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Big Data Course – Enrol Now.To learn more about Machine Learning Using Python and Spark – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with SAS Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Apache Spark Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Market Risk Analytics and Modelling Course – Enrol Now.