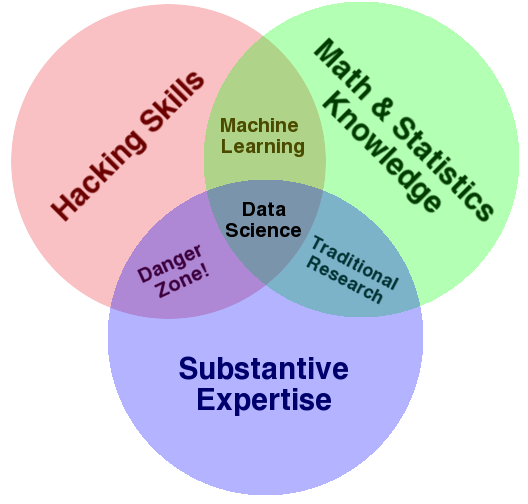
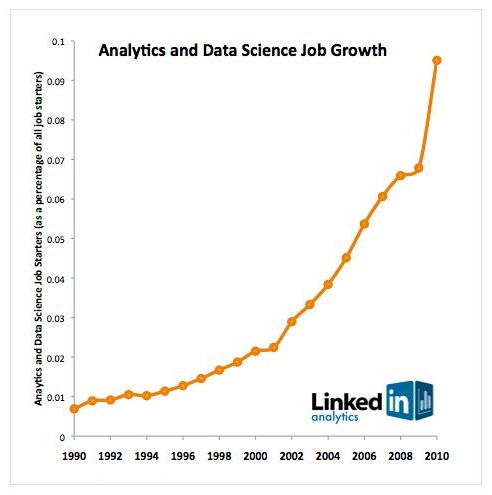
Data fires up everything, nowadays. And data science is gaining exceptional traction in the job world, as data analytics, machine learning, big data, and data mining are fetching relevance in the mainstream tech world. By 2025, it is being expected that data science industry will reach $16 billion in value – this is why landing a job in data science domain is the next big thing!
The skills you will imbibe as a data scientist would be incredible, powerful and extremely valuable. You can easily a bag a dream job in corporate moguls, like Coca-Cola, Uber, Ford Motors and IBM, as well as play a significant role in any pro-social or philanthropic endeavors to make this world a better place to live in.
Check out these extremely interesting fields you could start your career in data science:
Biotechnology
No wonder, science and medicine are intricately related to each other. As the technology pushes boundaries, more and more companies are recommitting themselves towards a better public health by nabbing biotechnology. Being a data scientist, you would help in unraveling newer ways of studying large amounts of data – including machine learning, semantic and interactive technologies. Eventually, they would influence treatments, drugs-usage, testing procedures and much more.

Energy
Power industry functions on data – and tons of it. Whether it’s about extracting mineral wealth from the earth’s crust or transporting crude oil or planning better storage facilities, the demand for data scientists is on the rise. Just as expanding oil fields ask for humongous amounts of data study, installing and refining cleaner energy production facilities relies on data about the natural environment and ways of modern construction. Data scientists are often given a ring to enhance safety standards and help companies recommit themselves towards better safety and environmental regulations.
Transportation
Recently, transportation is undergoing a robust change. For example, Tesla paved a new road of development and turned countless heads by unveiling a long-haul truck that could drive on its own. Though it’s not the first time, they are prone to lead the change.
Beyond self-driving vehicle technology, the transportation industry is looking for more efficient ways to preserve and transport energy. These advancements in technology works wonders when combined with better battery technology development – in simple terms, every individual field in transportation industry is believed to benefit from a motley team of data scientists.

Telecommunications
The internet is not only about tubes, but all about data. The future of the internet is here, with ever-increasing networks of satellites and user devices establishing communication through blockchain. Though they are yet to be used on large-scale, they have started making news. In situations like this, it would be difficult not to highlight the importance of data science and data architecture as they are becoming major influencers in the internet world. Whenever there is a dire need to make the public aware of a new product, we rely on user data – hence the role of data scientists is the key to a better future.
Today, data science is an interesting field to explore, and it is going to play an integral role as the stride in technology and globalization keeps expanding its base. If you have a keen eye for numbers, charts, patterns and analytics, this niche is perfectly suitable for you.
DexLab Analytics is a prime Data Science training institute Delhi that excels in offering advanced business analyst training courses in Gurgaon. Visit our official site for more information and make a mark in data analytics!
Interested in a career in Data Analyst?
To learn more about Data Analyst with Advanced excel course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with R Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Big Data Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Machine Learning Using Python and Spark – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with SAS Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Apache Spark Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Market Risk Analytics and Modelling Course – Enrol Now.