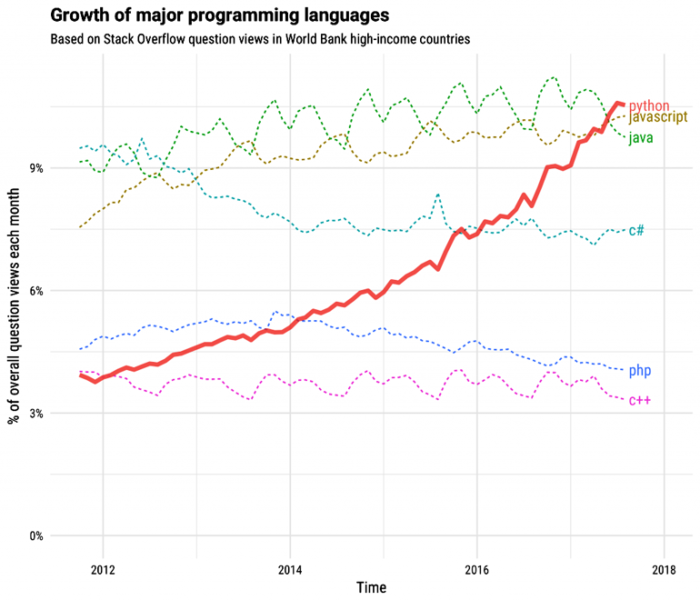
Python and data analytics are possibly three of the most commonly heard words these days. In today’s burgeoning tech scene, being skillful in these two subjects can prove very profitable. Over the years, we have seen the importance of Python education in the field of data science skyrocketing.
So here we present a general guide to help start off your Python learning:
Reasons to Choose Python:
Popularity
With over 40% data scientists preferring Python, it is clearly one of the most widely used tools in data analysis. It has risen in popularity above SAS and SQL, only lagging behind R.
General Purpose Language
There might be many other great tools in the market for analyzing data, like SAS and R, but Python is the only trustworthy general-purpose language valid across a number of application domains.
Step 1: Setup Python Environment
Setting up Python environment is uncomplicated, but a primary step. Downloading the free Anaconda Python package is recommended. Besides core Python language, it includes all the essential libraries, such as Pandas, SciPy, NumPy and IPython, and graphical installer also. Post installation, a package containing several programs is launched, most important one being iPython also known as Jupyter notebook. After launching the notebook, the terminal opens and a notebook is started in the browser. This browser works as the coding platform and there’s no need for internet connection even.
Step 2: Knowing Python Fundamentals
Getting familiar with the basics of Python can happen online. Active participation in free online courses, where video tutorials, practice exercises are plentiful, can help you grasp the fundamentals quickly. However, if you are seeking expert guidance, you must explore our Python data science courses.
Step 3: Know Key Python Packages used for Data Analysis
Since it is a general purpose language, Python’s utility stretches beyond data science. But there are plentiful Python libraries useful in data functionalities.
Numpy – essential for scientific computing
Matplotib – handy for visualization and plotting
Pandas – used in data operations
Skikit-learn – library meant to help with data mining and machine learning activities
StatsModels – applied for statistical analysis and modeling
Scipy-SciPy – the Numpy extension of Python; it is a set of math functions and algorithms
Theano – package defining multi-dimensional arrays.
Step 4: Load Sample Data for Practice
Working with sample datasets is a great way of getting familiar with a programming language. Through this kind of practice, candidates can try out different methods, apply novel techniques and also pinpoint areas of strength and in need of improvement.
Python library StatModels contains preloaded datasets for practice. Users can also download dataset from CSV files or other sources on web.
Step 5: Data Operations
Data administration is a key skill that helps extract information from raw data. Majority of times, we get access to crude data that cannot be analyzed straightaway; it needs to be manipulated before analyzing. Python has several tools for formatting, manipulating and cleaning data before it is examined.
Step 6: Efficient Data Visualization
Visuals are very valuable for investigative data analysis and also explaining results lucidly. The common Python library used for visualization is Matplotlib.
Step 7: Data Analytics
Formatting data and designing graphs and plots are important in data analysis. But the foundation of analytics is in statistical modeling, data mining and machine learning algorithms. Having libraries like StatsModels and Scikit-learn, Python provides all necessary tools essential for performing core analyzing functions.
Concluding
As mentioned before, the key to learning data analytics with Python is practicing with imported data sets. So without delay, start experimenting with old operations and new techniques on data sets.
For more useful blogs on data science, follow DexLab Analytics – we help you stay updated with all the latest happenings in the data world! Also, check our excellent Python courses in Delhi NCR.
Interested in a career in Data Analyst?
To learn more about Data Analyst with Advanced excel course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with R Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Big Data Course – Enrol Now.To learn more about Machine Learning Using Python and Spark – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with SAS Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Apache Spark Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Market Risk Analytics and Modelling Course – Enrol Now.