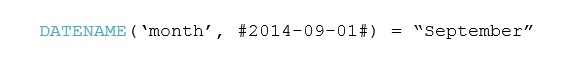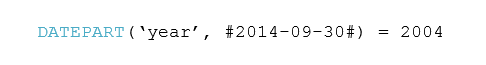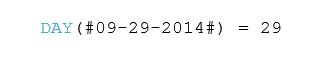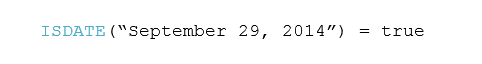According to Google Search, ‘blockchain’ is defined as “a digital ledger in which transactions made in bitcoin or in other cryptocurrency is recorded chronologically and publicly.”
Speaking in a way of cryptocurrency, a block is a record of new transactions that could mean the actual location of cryptocurrency. Once each block has completed its transaction, it’s added to the chain, creating a chain of blocks known as blockchain.
Suppose a Google spreadsheet is shared by each and every computer which is connected to the internet in this world. When a transaction happens, it will be recorded in a row of this spreadsheet. Just like a spreadsheet has rows, Blockchain consists of Blocks for each transaction.
Whoever has access to a computer or mobile can connect to the internet and can have access to the spreadsheet and add a transaction, but the spreadsheet doesn’t permit anyone to edit the information which is already available. No third party can interfere into its transactions, therefore saves time and conflict.

Types of Blockchains:
- Open and permission-less: Public and permissionless blockchains look like bitcoin, the first blockchain. All exchanges in these blockchains are open and no authorizations are required to join these circulated elements.
- Private and permission: These blockchains are constrained to assigned individuals, exchanges are private, and authorization from a proprietor or supervisor substance is required to join this system. These are frequently utilized by private consortia to oversee industry esteem chain openings.
- Hybrid blockchains: An extra region is a developing idea of sidechain, which takes into consideration distinctive blockchains (open or private) to speak with each other, empowering exchanges between members crosswise over blockchain systems.
Various Applications Of Blockchain Are As Follows:
a) Smart Contracts:
Smart Contracts eases the way we exchange money, property, shares and avoids third person/party conflicts. Smart keys access can only be permitted to the authorized party. Basically, computers are given the command to control the contracts and to release or hold the funds by giving the keys to the permitted persons.
For example, if I want to rent an office space from you, we can do this in blockchain using cryptocurrency. You will get a receipt which is saved in the virtual contract and I will get the digital entry key which will reach me by a specified date. If you send the key before the specified date, the function holds it and releases both receipt and the key when the date arrives.
If I receive the key I surely should pay you. And this contract will be canceled when the time gets complete, and it cannot interfere as all the participants will be alerted. The Smart contracts can be used for insurance premiums, financial derivatives, financial services, legal processes etc.
b) Digital Identity:
The future of blockchain will be blooming in the coming years. Blockchain technologies make both managing and tracking digital identities reliable and systematic, resulting in easy registering and minimizing fraud.
Be it national security, citizenship documentation, banking, online retailing or healthcare, identity authentication and authorization is a process entangled in between commerce and culture, worldwide. Introducing blockchain into identity-based mechanisms can really bring captivating solutions to the security problems we have online.
Blockchain technology is known to offer a solution to many digital identity issues, where identity can be uniquely validated in an undeniable, unchangeable, and secured manner.
Present-day methods involve problematic password-based systems of known secrets which are exchanged and stored on insecure computer systems. Blockchain-based certified systems are actually built on undeniable identity verification for using digital signatures based on the public key related cryptography.
In blockchain identity confirmation, the only check that is performed is to know if the transaction was signed by the authorized private key. It is implied to whoever has access to the private key is the owner and the exact identity of the owner is deemed unrelated.
c) Insurance:
Claims dealing can be disappointing and unrewarding. Insurance agents need to go through deceitful cases and deserted approaches, or divided information sources for clients to express a few – and process these documents manually. Space for mistake is enormous. The blockchain gives an ultimate framework for hazard-free administration and clarity. Its encryption properties enable insurers to represent the ownership to be protected.
“This will be the toughest on the portions of the industry that are least differentiated, where consumers often decide based on price: auto, life, and homeowner’s insurance.” — Harvard Business Review
d) Supply-Chain Communications and Proof-of-Provenance:
The majority of the things we purchase aren’t made by a single organization, yet by a chain of providers who offer their ingredients (e.g., graphite for pencils) to an organization that gathers and markets the final commodity. On the off chance that any of those commodities flops, in any case, the brand takes the brunt of the backfire — it holds most of the duty regarding its supply chain network.
However, consider the possibility that an organization could proactively give carefully perpetual, auditable records that show stakeholders the condition of the item at each esteem included process.
This is not a little task: The worldwide supply chain network is evaluated to be worth $40 trillion; and from a business-process point of view, it’s a fabulously incapable chaos. As a related issue, blockchain can be utilized to track diamonds, creative skill, real estate, and practically any other resources.
e) Music Industry:
While music lovers have hailed digitization as the popular government of the music business, 15.7 billion dollar music industry is confusingly continuing as before. Music piracy through unlawfully downloaded, duplicated and shared content eats into the artist’s sovereignties and music labels’ income. Added to this, is the absence of a vigorous rights administration framework, which prompts loss of income to the artist.
Also, the income, when it really achieves the artist, can take up to two years! Another region of concern is unpaid sovereignties, which are frequently suspended in different stages because of missing data or rights possession. There is additionally an absence of access to continuous advanced sales information, which if accessible can be utilized to strategize advertising efforts more successfully.
These very zones are the place Blockchain can have stunning effects. As a publically accessible and decentralized database that is distributed over the web, Blockchain keeps up lasting and undeletable records in cryptographic format. Exchanges happen over a peer to peer system and are figured, confirmed and recorded utilizing a computerized agreement strategy, disposing of the requirement for an intermediator or outsider to oversee or control data.
The very engineering of Blockchain being unchanging, dispersed and distributed conveys enormous potential to manage the present troubles influencing the music business.
An essential region in which Blockchain can bring out positive change is in the formation of a digital rights database. Digital rights articulation is one of the basic issues distressing the present music industry. Recognizing copyright of a melody and characterizing how sovereignties ought to be part of musicians, entertainers, distributors, and makers are troublesome in digital space. Regularly artists miss out on sovereignties because of complicated copyright condition.
Blockchain’s changeless distributed ledger framework, which guarantees that no single organization can assert proprietorship, ensures an ideal arrangement. Secure documents with all applicable data, for example, structure, versus, straight notes, cover craftsmanship, permitting, and so on, can be encoded onto the Blockchain making a changeless and inerasable record.
f) Government and Public records:
The administration of public services is yet another region, where blockchain can help diminish paper-based procedures, limit fraud, and increment responsibility amongst specialists and those they serve.
Some US states are volunteering to understand the advantages of blockchain: the Delaware Blockchain Initiative propelled in 2016, expects to make a proper legitimate foundation for distributed ledger shares to increase productivity and speed of consolidation administrations.
Illinois, Vermont, and different states have since reported comparative activities. Startup companies are sponsoring in the effort also: in Eastern Europe, the BitFury Group is presently working with the Georgian government to secure and track government records.
Conclusion:
This article focused on the blockchain and its applications in various industries explains challenges and potentials and how people can secure their information digitally without any issues and increasing their ability. As these applications are still under development and yet to be untangled in the future, blockchain could become a powerful tool conducting fair trade, improving business and supporting the society.
To never miss a beat of technology related news and feeds – follow DexLab Analytics. We are a team of experts offering state of the art business analyst training courses in Gurgaon. Not only that, we provide a plethora of machine learning and Hadoop courses too for all the data-hungry candidates. So, drop by and quench your thirst for data from us!
About the Author:
 K.Maneesha is an SEO Developer At Mindmajix.com. She holds a masters degree in Marketing from Alliance University, Bangalore. Maneesha is a dog-lover and enjoys traveling with friends on trips. You can reach her at manisha.m4353@gmail.com. Her LinkedIn profile Maneesha Kakulapati.
K.Maneesha is an SEO Developer At Mindmajix.com. She holds a masters degree in Marketing from Alliance University, Bangalore. Maneesha is a dog-lover and enjoys traveling with friends on trips. You can reach her at manisha.m4353@gmail.com. Her LinkedIn profile Maneesha Kakulapati.
Interested in a career in Data Analyst?
To learn more about Machine Learning Using Python and Spark – click here.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Advanced excel course – click here.
To learn more about Data Analyst with SAS Course – click here.
To learn more about Data Analyst with R Course – click here.
To learn more about Big Data Course – click here.





 K.Maneesha is an SEO Developer At
K.Maneesha is an SEO Developer At