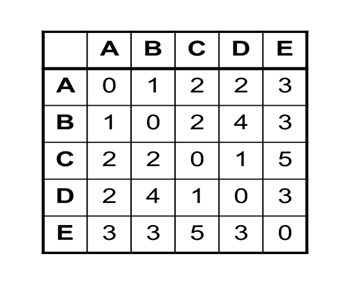
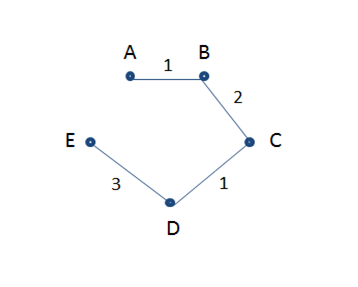
The volume of data is expanding at an enormous rate, each day. No more are 1s and 0s are petty numerical digits, they are now a whole new phenomenon – known as Big Data. A fair assessment of the term helped us understand the massive volume of corporate data collected from a broad spectrum of sources is what big data is all about.
A recent report suggested that organizations are expected to enhance their annual revenues by an average of $5.2 million – thanks to big data.
More about Data, Rather Big Data
Back in the day, most of the company information used to be stored in written formats, like on paper. For example, if 80% of confidential information was kept on paper, 20% was stored electronically. Now, out of that 20%, 80% was kept in databases.
With time, things have changed. Across the business domain, more than 80% of companies store their data in electronic formats nowadays, and at least 80% of that is found outside databases, because most organizations prefer storing data in ad hoc basis in files at random places.
Now, the question is what kind of data is of crucial importance? Data, that impacts the most?
With that in mind, we’ve three kinds of data:
- Customer Data
- IT Data
- Internal Financial Data
The Value of Data
For companies, data means dollars – the way data costs companies’ their time and resources, it also leads to increased revenue generation. However, the key factor to be noted here is – the data have to be RELEVANT. Despite potential higher revenues through advanced data skills and technology implementation, an average enterprise is only able to employ 51% of total accumulated and generated data, and less than 48% of decisions are based on that.
To say the least, unlike before, today’s organizations gather data from a wide array of sources – CCTV footage, video-audio files, social networking data, health metrics, blogs, web traffic logs and sensor feeds – previously companies were not as efficient and tech-savvy as they are now. In fact, five years ago, some of the sources from which data is accumulated did not even exist nor were they available on corporate radar.
With the rise of ingenious and connected technologies, companies are turning digital. It hardly matters if you are an automobile manufacturer, fashion collaborator or into digital marketing – being connected digitally and owning meaningful data is all to cash on. You can structure intricate database just with consumers’ details, both personal and professional, such as age, gender, interests, buying patterns, behavioral statistics and habits. Remember, accumulating and analyzing data is not only productive for your company but also becomes a saleable service in its own way.
Make Data the Bedrock of Your Business
Data has to be the life and blood of business plans and decisions you want to make. Ensure your employees learn about the value of data collection, make sure you align your IT resources properly and keep pace with the latest data tools and technologies as they tend to keep on changing, constantly.
Embrace the change – while physical assets are losing importance, data appears to be the most valuable asset a company can ever have.
For big data hadoop certification in gurgaon, look no further than DexLab Analytics. With the right skills in tow and adequate years of experience, this analytics training institute is the toast of the town. For more information, visit our official page.
The blog has been sourced from:
https://www.techrepublic.com/blog/cio-insights/big-data-cheat-sheet/
https://www.techrepublic.com/article/the-3-most-important-types-of-data-for-your-business
Interested in a career in Data Analyst?
To learn more about Data Analyst with Advanced excel course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with R Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Big Data Course – Enrol Now.To learn more about Machine Learning Using Python and Spark – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with SAS Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Apache Spark Course – Enrol Now.
To learn more about Data Analyst with Market Risk Analytics and Modelling Course – Enrol Now.